STD X – STUDY OF COMPOUNDS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE ACID – NEWTON
About Course
In this section will learn this following chapters:
1.HYDROGEN CHLORIDE
Last Updated:June 6, 2024
0 (0 Ratings)
Share Course
Page Link
Share on social media
Description
Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride
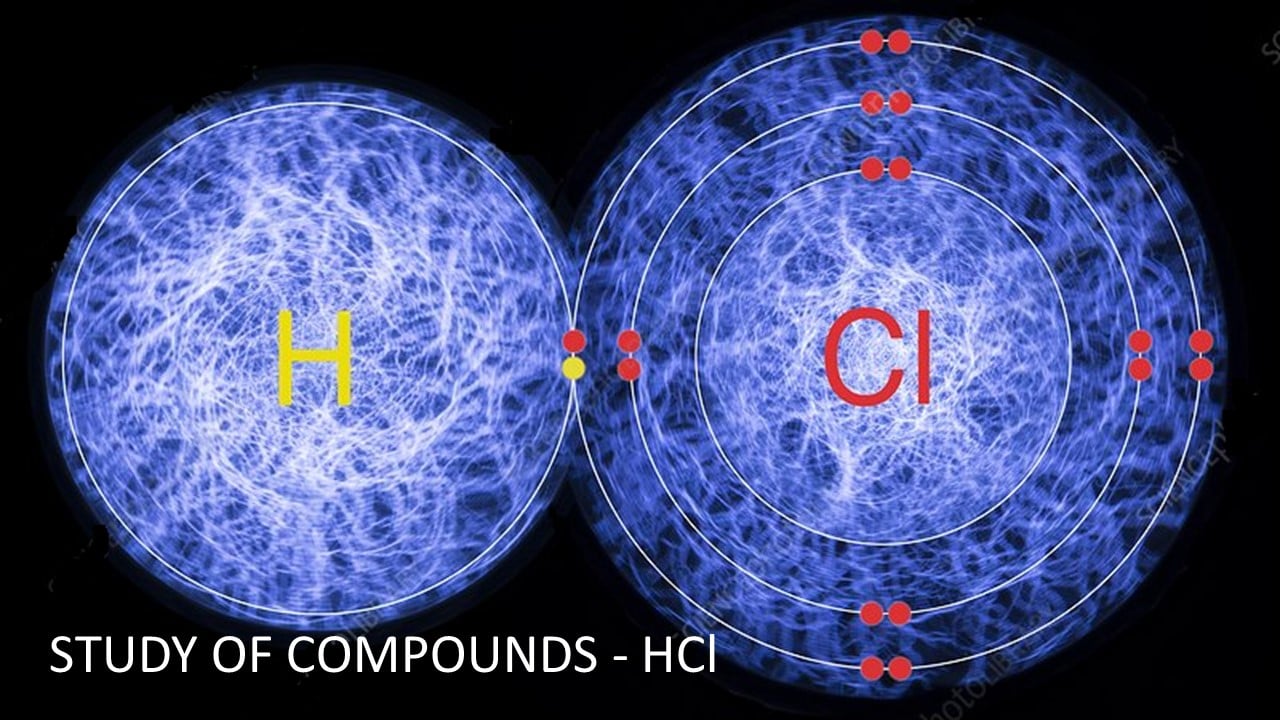
Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl. It was discovered in 1648.
Hydrogen Chloride occurs in a free state in volcanic gases and in gastric juices of mammals.
It is a compound of the elements hydrogen and chlorine.
Molecular formula is HCl and Molecular mass is 36.5
At room temperature, it is a colourless, pungent gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity.
It condenses at -85° C (-121° F) and freezes at -114° C (-173° F). The gas is highly soluble in water. Because of its high solubility, the gas fumes in moist air.
Hydrogen chloride is mostly used in the production of hydrochloric acid. It is useful in the preparation of aqua regia, in the manufacture
Properties and test of Hydrogen Chloride
Hydrogen Chloride is a Diatomic Molecule which consists of two atoms. It is a compound of the elements hydrogen and chlorine,
Hydrogen Chloride is a colourless, poisonous gas with an unpleasant, acrid odour. It is highly soluble in water and readily soluble in alcohol and ether. It fumes in moist air. It is not flammable, and the liquid is a poor conductor of electricity.
When hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved in water, hydrochloric acid is formed.
Molecular Formula: HCl
Molecular Mass: 36.5
Bond; Covalent.
Melting Point: -114 deg C
Boiling Point: -85 deg C
Formula weight 36.46
Specific gravity or density 1.2
Flash Point: none
Reaction with ammonia
When a rod dipped in ammonia is brought near vapours of HCl, dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed. This is also a confirmatory test for HCl
Free
Free
Free access this course
-
LevelIntermediate
-
Total Enrolled3
-
Last UpdatedJune 6, 2024
Hi, Welcome back!
Material Includes
- 🔥 Live Interactive classes with in-class doubt solving
- ⭐ Weekly Test and Quiz with instant tracking for progress
- ⚙️ Revision of the course after testing
- 👋 Fortnightly Parents and Tutor interactions
- 🌷 Expert monitoring of student's learning progress
- 👨👩👧👧 Daily communication over call, whatsapp and mail
- 💻3 hours on-demand video
- ✍4 downloadable resources
- ⌛Access for entire Academic Year
- 📱Access on mobile and Desktop
- 📋Assignments and review of the same
- 💡Tests and Correction by Board paper checkers
- 🏅Certificate of completion and Live tracking with Grade book
Course Duration:
0
Course level:Intermediate
Enrolled:3
About Course
In this section will learn this following chapters:
1.HYDROGEN CHLORIDE
Course Curriculum
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE – 08 – MAY – INTRODUCTION TO HCL
-
STUDY OF COMPOUND HCL – PHYSICAL CLASS – INTRODUCTION TO HYDROGEN CHLORIDE GAS
23:23 -
STUDY OF COMPOUNDS – PREPARATION OF HYDROGEN CHLORIDE FROM SODIUM CHLORIDE
02:53 -
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE – CORE CONCEPT – CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF HYDROGEN CHLORIDE GAS
05:41 -
STUDY OF COMPOUND HCI ACID – PHYSICAL CLASS – CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF HYDROGEN CHLORIDE
09:52 -
STUDY OF COMPOUND HCl – PHYSICAL CLASS – COLLECTION PURIFICATION AND FOUNTAIN EXPERIMENT
17:00 -
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE – CORE CONCEPT – TEST FOR HYDROGEN CHLORIDE
04:32 -
STUDY OF COMPOUND HCL ACID – PHYSICAL CLASS – PREPARATION OF HYDROCHLORIC ACID
20:06 -
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE – CORE CONCEPT – CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF HYDROCHLORIC ACID
16:02 -
STUDY OF COMPOUND HCl – PHYSICAL CLASS – CHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND TESTS FOR HYDROCHLORIC ACID
21:21 -
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE – CORE CONCEPT – LET’S RECALL
30:46
STUDY OF COMPOUNDS – HCI – 18 MAY 2024
-
STUDY OF COMPOUNDS – PHYSICAL CLASS – HCl – CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CONCENTRATED HCl
18:31 -
STUDY OF COMPOUNDS – PHYSICAL CLASS – HCl – CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF DILUTE HCl
16:21 -
STUDY OF COMPOUNDS – PHYSICAL CLASS – HCl – FOUNTAN EXPERIMENT AND PREPARATION OF HYDROCHLORIC ACID
14:59 -
STUDY OF COMPOUNDS – PHYSICAL CLASS – HCl -OCCURANCE AND GENERAL METHOD OF PREPARATION
23:23
Student Ratings & Reviews

No Review Yet

